STEEL WIRE ROPES
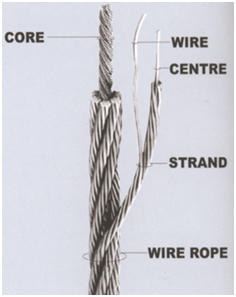
A wire rope consists of a number of wire strand formed helically about a central axis. The most popular ropes have six or eight strands supported by an axial member known as the core. There are other constructions, but they are less common. Each strand is composed of a number of individual wires which have been formed helically about an axial member called the center. This center supporting member of the strand is generally one or more wires; however, it may be natural fibers (cotton, hemp, sisal, etc.) or synthetic fibers (rayon, nylon, polypropylene).
Stainless steel wire
Wire ropes made of stainless steel wire are extremely resistant to corrosion and moreover, to temperature up to 1050˚C. Originally only the AISI types 304 and 302 were used for rope making but today almost all our stainless steel wire ropes are made of steel according to AISI type 316 which has better mechanical properties and a higher resistance to electrolytic corrosion, which increased resistance to sea water.
Tensile strengths of steel wire
Steel wire is made in various tensile strength to meet the different requirements of a particular job. For the production of our ropes,
We use wire in the following tensile strength ranges:
1470 N/mm² (150 kgf/mm²)
1570 N/mm² (160 kgf/mm²)
1770 N/mm² (180 kgf/mm²)
1960 N/mm² (200 kgf/mm²)
2160 N/mm² (220kgf/mm²)
Tensile grades
Manufacturing Standards
Rope cores
Ropes are supplied either with fiber or steel core, the choice being largely dependent on the application.
Fiber Core
Fiber cores are mainly made from polypropylene. This material has the advantage that it neither absorbs nor retains moisture, and thus it eliminates conditions creating internal corrosion. Polypropylene core will have small variations in size and weight and are less susceptible to damage, especially under moist conditions.
The following precautions must be taken during use:
– Do not use fiber core ropes where these are exposed to high temperatures, i.e. above 90˚c; this will damage the fiber core.
– The fiber core ropes should not be used when multi – layer winding is required as the fiber cores susceptible to crushing.
Steel core
The steel core is designated IWRC (Independent Wire Rope Core) and normal construction is 7X7. Steel core proves advantageous in severe working conditions involving a low factor of safety, small drums and sheaves, high operational speeds and wide fleet angles. Steel core tends to preserve the circular cross-section of the ropes when it is crushed by over-winding on drums .It also prevents the strand from bridging, (being forcibly against each other) which can result in fatigue failure of wires.
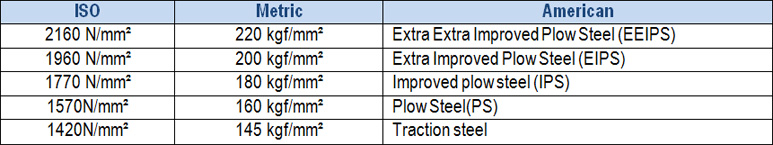
Wire rope lay
The direction of lay or rotation of the strands is normally right hand .But some machinery needs left hand lay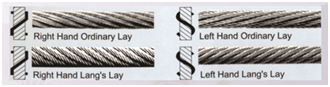
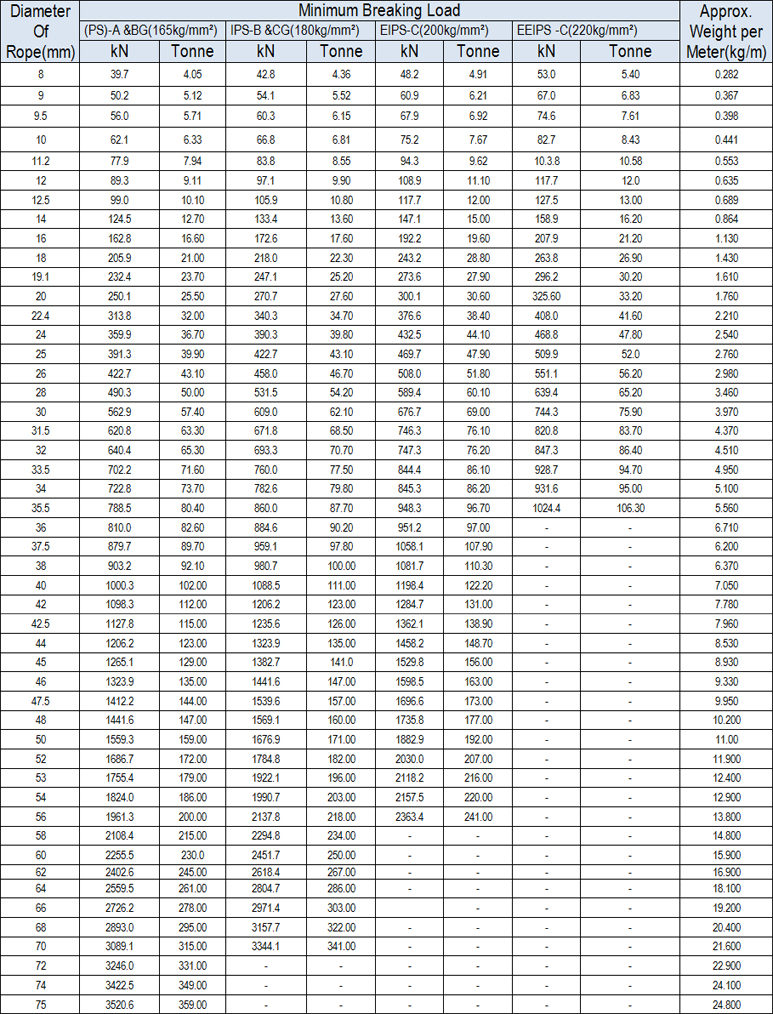
Diameter of wire ropes
The diameter of wire ropes is the diameter of circle which encloses all of the wires .When measuring wire rope it is important to take the greatest distance of the outer limit of the crowns of two opposite strands .A measurement across the valleys will result incorrect lower readings.
Method of measuring diameter
Caliper, fitted with jaws broad enough to cover not less than two adjacent strands
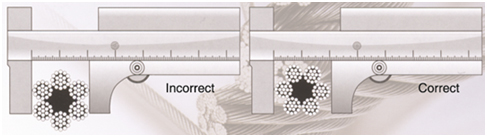

Safety factor of wire rope
It is difficult to fix the safety factor for each type of wire rope to be used for various equipments, as this factors depends not only on the load carried, but also on the speed of rope working, the kinds of fitting used for rope ends, the acceleration and deceleration, length of rope, the number, size and arrangements of sheave and drums etc. The following safety factors are minimum requirements for safety and economy in the common installation.
HANDLING AND INSTALLATION
The following guidelines must be taken care for a longer life of wire rope.
- Twist, loop or kink of wire rope.
- Moisture, dust and acid or sulphuric hume gas.
- Overload
- Crushing or hammering.
- Sever or reverse bending (S-Bending).
- Too small sheaves, drums and guide rollers.
- Hard rolling of sheaves and guide rollers.
- Worn groove, broken or soft sheaves and rollers.
- Poor or no lubrication.
- Wrong fitting and spooling on the drum.
- Excessive fleet angle.
- Vibration.
- Obstacles, sand and grit on the surface of operation line.
- Shock too fast start or stop.
- Heat influence.
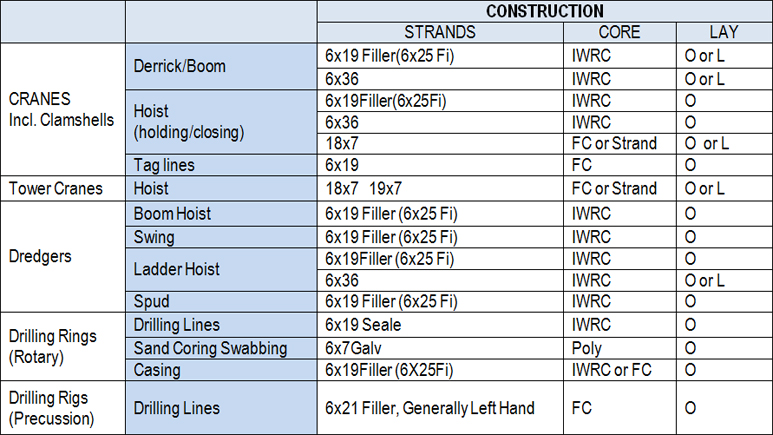
DIFFERENT STEEL WIRE ROPE CONSTRUCTIONS AND APPLICATIONS.
These suggestions should therefore be taken as a guide where no other guidance exists or as possible
alternatives where one construction has been found unsatisfactory.
CROSS SECTIONS OF STEEL WIRE ROPE
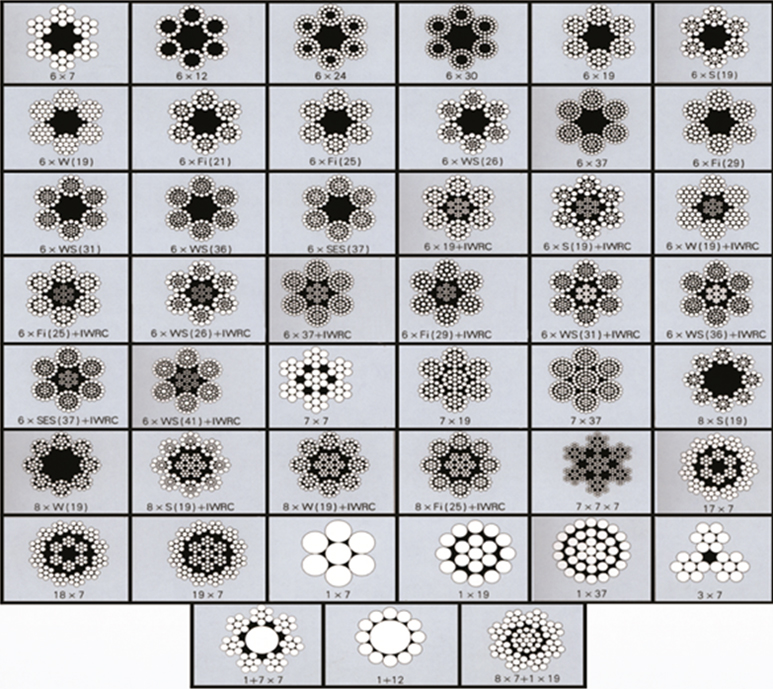
STEEL WIRE ROPE CONSTRUCTIONS
Construction:
6 Strands
29, 31, 36, 41, 37, Wires per strand
Independent Wire Rope Core
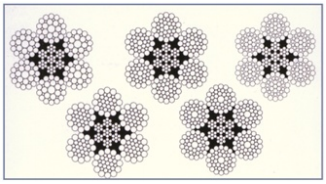
6 x FI (29), WS (31), (36), (41), SES +IWRC
POWERFLEX ROPE
By flattening the surface of outer wires of each strand, this plane contacting Lay construction has flat / touches area of outer wire comparing round strand types rope.
This flat touch area enables longer life of each wire before breaking. While designing this construction, it is emphasized the optimal balance between high tensile strength, fatigue resistance, abrasion resistance, and structural stability. Power flex rope is widely used in various applications such as crane, fishing and mining.
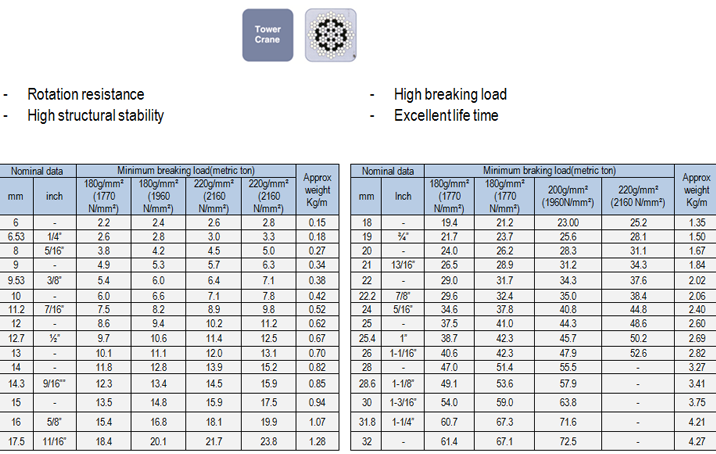
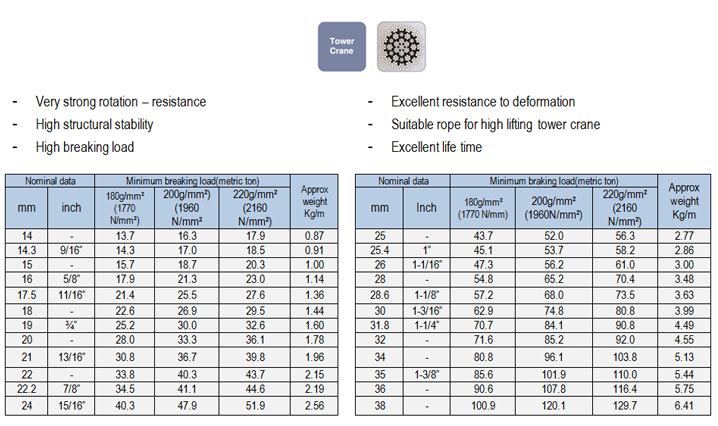
POWERFLEX 37,37L

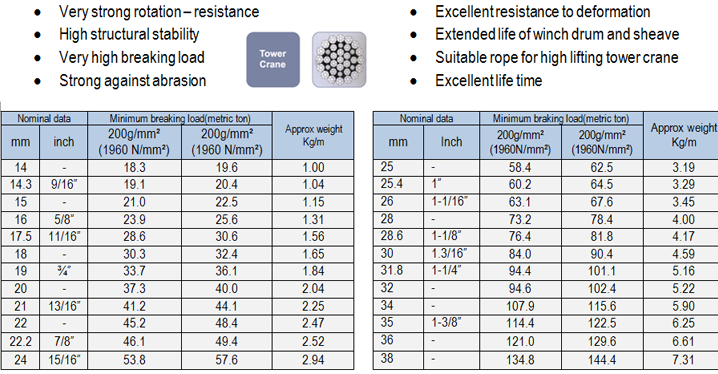
- Very strong rotation – resistance
- High structural stability
- Very high breaking load
- Strong against abrasion
- Excellent resistance to deformation
- Extended life of winch drum and sheave
- Suitable rope for high lifting tower crane
- Excellent life time
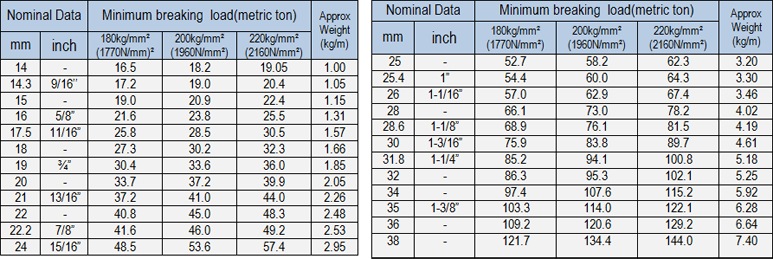
POWERFLEX 35,35L
POWERLIFT 35,35L (Non – Rotating)
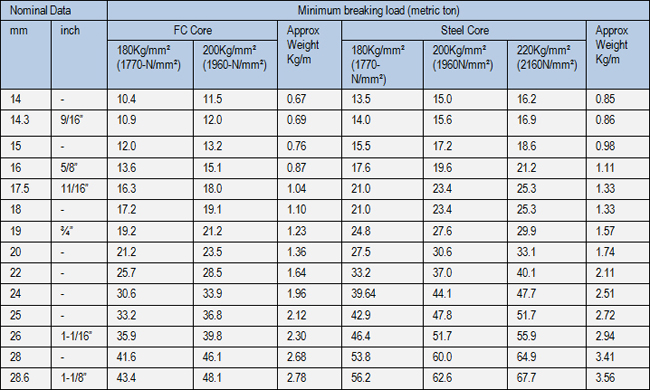
POWERLIFT 19
Crane/Logging/Shipping/Fishing/General Engineering/ General purpose
6X19 Class rope
CRANE / DRILLING / ENGINEERING / ELEVATOR
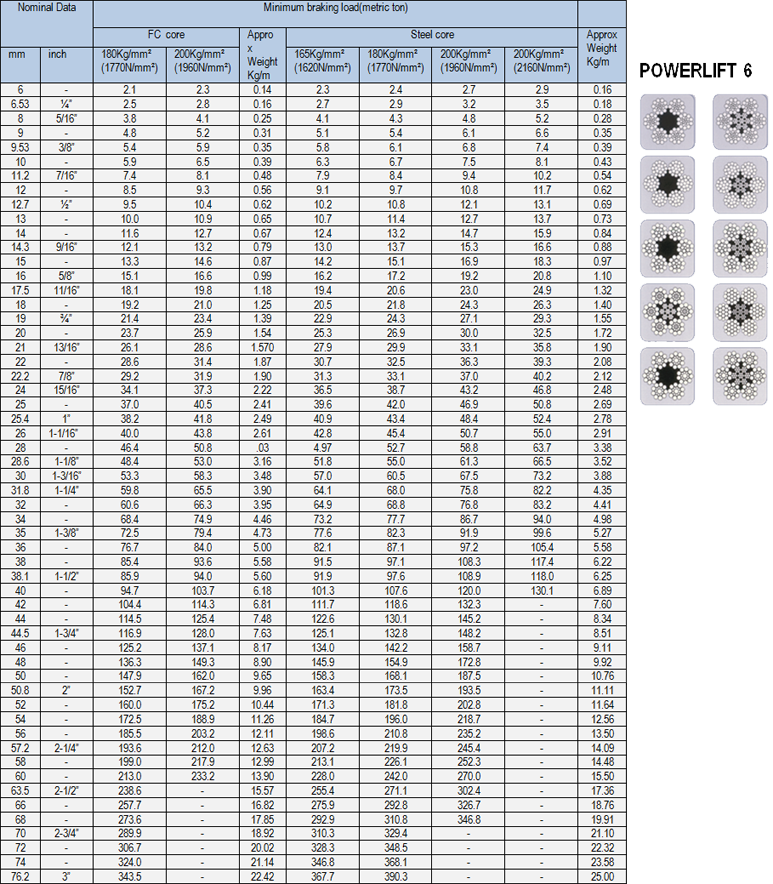
POWERLIFT 8
Crane/Drilling
General purpose

 ◄ 8x19Class Rope
◄ 8x19Class Rope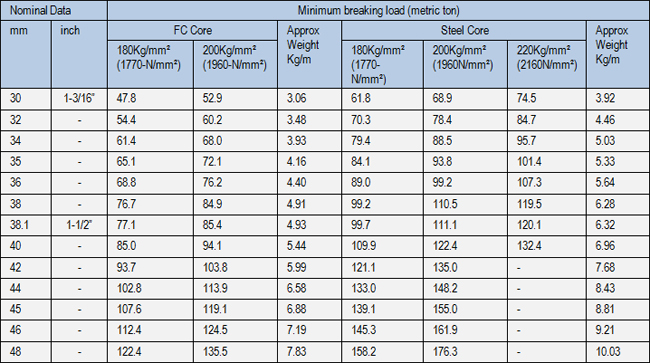 ◄ 8x19Class Rope
◄ 8x19Class RopeCrane / Drilling / Engineering / Elevator
POWERLIFT 8
Crane/Drilling
General purpose

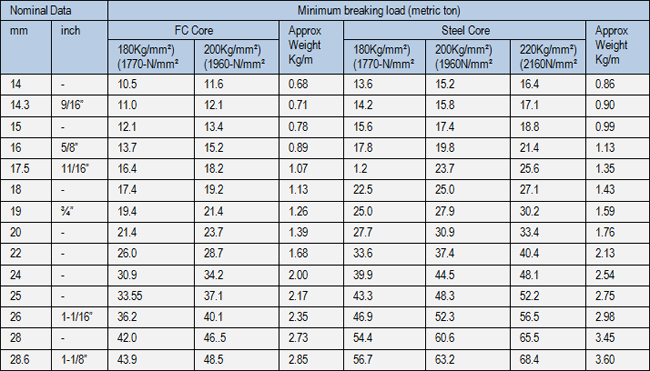 ◄ 8x37Class Rope
◄ 8x37Class Rope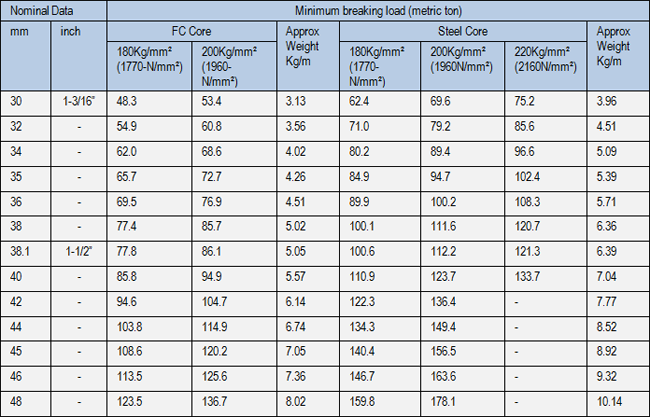 ◄ 8x37Class Rope
◄ 8x37Class Rope